Name
ST_CleanPolygon — Cleans polygons o multipolygons to be topologically corrects. So, enforces them to be valid geometries.
Synopsis
geometry ST_CleanPolygon(bytea
Polygon);
Description
Cleans polygons o multipolygons to be topologically corrects. So, enforces them to be valid geometries (ST_IsValid). OGC states the rules that define valid polygons.
It is computed without tolerances.
Coordinate Dimensions
| 2D | 3D | M |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
Spatial Standards Support
| OGC SFS for SQL. 1.1 (1999) | OGC SFS for SQL. 1.1.0 (2005) | OGC SFS for SQL. 1.2.0 (2006) | SQL-MM Part 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - |
Examples
POLYGON
The Interior of every Polygon should be a connected point set.
SELECT ST_AsText( ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('POLYGON ((2 2, 2 6, 7 6, 7 2, 2 2),(2 2, 6 2, 7 4, 5 3, 6 2, 2 2))'))); --Result POLYGON ((6 2, 2 2, 2 6, 7 6, 7 4, 7 2, 6 2))GeomA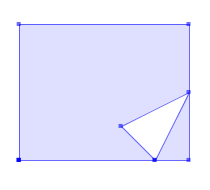 ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)
ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)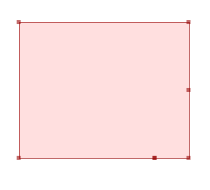
The boundary of a Polygon may intersect at a Point but only as a tangent (i.e. not on a line)
SELECT ST_AsText( ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('POLYGON ((2 2, 2 6, 7 6, 7 2, 2 2), (3 2, 3 3, 4 3, 4 2, 3 2))'))); --Result POLYGON ((2 2, 2 6, 7 6, 7 2, 4 2, 3 2, 2 2))GeomA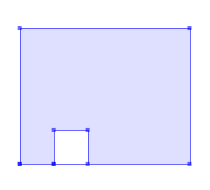 ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)
ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)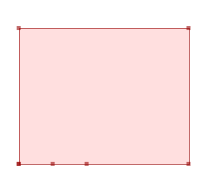
A Polygon may not have cut lines, spikes or punctures:
SELECT ST_AsText( ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('POLYGON ((3 2, 3 6, 7 6, 7 4, 8 4, 7 4, 7 2, 3 2))'))); --Result POLYGON ((3 2, 3 6, 7 6, 7 4, 7 2, 3 2))GeomA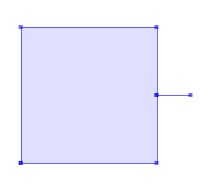 ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)
ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)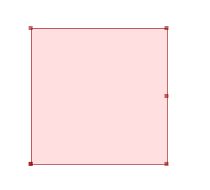
Each hole should be a connected component of the Exterior.
SELECT ST_AsText( ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('POLYGON ((1 1, 1 4, 3 4, 3 1, 1 1), (4 2, 4 4, 6 4, 6 2, 4 2))'))); --Result MULTIPOLYGON (((1 1, 1 4, 3 4, 3 1, 1 1)), ((4 2, 4 4, 6 4, 6 2, 4 2)))GeomA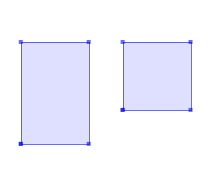 ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)
ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)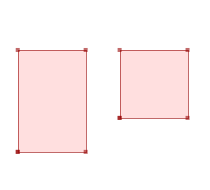
MULTIPOLYGON
The interiors of 2 Polygons that are elements of a MultiPolygon may not intersect.
SELECT ST_AsText( ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('MULTIPOLYGON (((1 1, 1 4, 4 4, 4 1, 1 1)), ((3 2, 3 5, 6 5, 6 2, 3 2)))'))); --Result POLYGON ((4 2, 4 1, 1 1, 1 4, 3 4, 3 5, 6 5, 6 2, 4 2))GeomA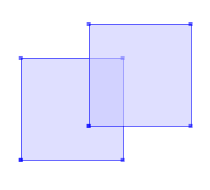 ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)
ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)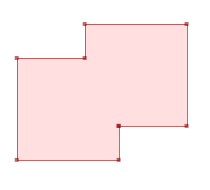
The Boundaries of any 2 Polygons that are elements of a MultiPolygon may not ‘cross’ and may touch at only a finite number of points. (Note that crossing is prevented by assertion 1 above).
SELECT ST_AsText( ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('MULTIPOLYGON (((1 1, 1 4, 3 4, 3 1, 1 1)), ((3 2, 3 4, 5 4, 5 2, 3 2)))'))); --Result POLYGON ((3 4, 5 4, 5 2, 3 2, 3 1, 1 1, 1 4, 3 4))GeomA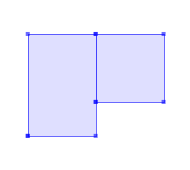 ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)
ST_CleanPolygon(GeomA)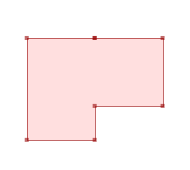
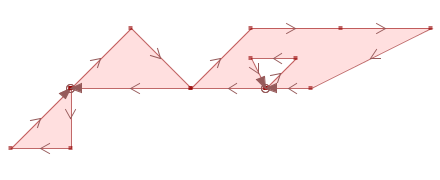
The following example of cleaning a polygon is more complex . There are repeated vertexes, changes of direction etc, The resulting geometry is a MultiPolygon composed of three Polygons.
SELECT ST_AsText(
ST_CleanPolygon(ST_GeomFromText('POLYGON ((13 8, 16 8, 13 8, 10 8, 8 6, 6 8, 2 4, 4 4, 4 6, 12 6, 16 8, 13 8),
(10 7, 10.5 6, 11.5 7, 10 7))')));
--Result
MULTIPOLYGON (((10.5 6, 8 6, 10 8, 13 8, 16 8, 12 6, 10.5 6), (10.5 6, 11.5 7, 10 7, 10.5 6)), ((4 6, 4 4, 2 4, 4 6)), ((4 6, 6 8, 8 6, 4 6)))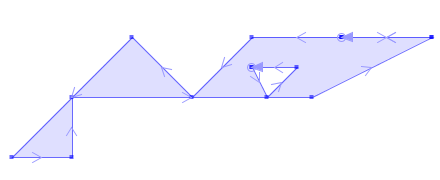 |
 |