Name
ST_Contains — Tests if a Geometry A spatially contains another Geometry B.
Synopsis
boolean ST_Contains(bytea GeomA, bytea GeomB);
Description
Tests if a Geometry A spatially contains another Geometry B, returns TRUE if so. The ST_Contains predicate has the following equivalent definitions:
Geometry A contains Geometry B if no points of B lie in the exterior of A, and at least one point of the interior of B lies in the interior of A.
ST_Contains is the inverse of ST_Within. a.Contains(b) «-» b.Within(a)
In mathematical terms:
a.Contains(b) «-» (I(a)∩I(b) ≠ ᴓ) Ʌ (E(a)∩I(b) =ᴓ) Ʌ (E(a)∩B(b) =ᴓ) ) «-» a.Relate(b, ‘T*****FF*’)The DE-9IM Intersection Matrix for the two geometries matches [T*****FF*]
Consequently and subtly, a LineString which is completely contained in the boundary of a Polygon is not considered to be contained in that Polygon because they don't share any interior points.
![[Caution]](images/caution.png) | |
This method does not support GeometryCollection arguments |
Coordinate Dimensions
| 2D | 3D | M |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
Spatial Standards Support
| OGC SFS for SQL. 1.1 (1999) | OGC SFS for SQL. 1.1.0 (2005) | OGC SFS for SQL. 1.2.0 (2006) | SQL-MM Part 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1.1.2 , 2.1.13.3 | 7.2.19.1 | 7.2.8.1 | 5.1.31 |
Examples
--Line-Point
SELECT ST_Contains(Line,Point) from
(SELECT ST_GeomFromText('LINESTRING (0 0, 10 10, 10 5, 15 10)') as Line, ST_GeomFromText('POINT (5 5)') as Point)as foo;
--Result
TRUEST_Contains(A,B) returns True in the following situations
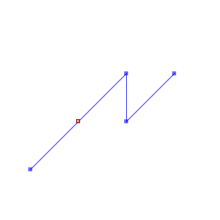 | 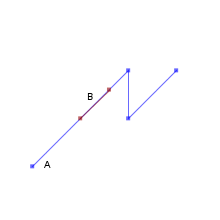 | |
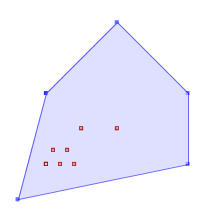 | 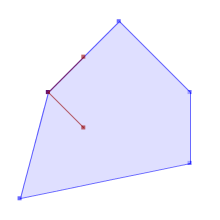 | 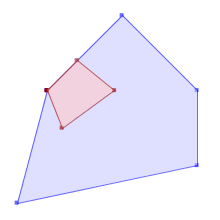 |
ST_Contains(A,B) returns False in the following situations
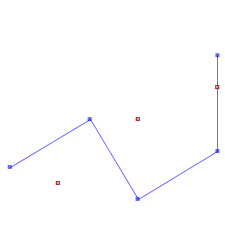 | 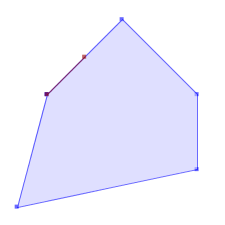 | 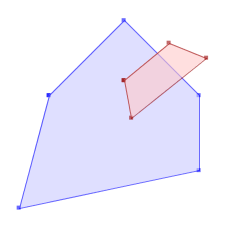 |